-
Seedshop
-
Feminized
Cannabis seeds -
Autoflowering
Cannabis Seeds -
Regular
Cannabis Seeds -
F1 Hybrid
Cannabis Seeds -
CBD
Cannabis Seeds -
Zamnesia
Cannabis Seeds
-
Top 10’s
- Top 10 Feminized Seeds
- Top 10 Autoflowering Seeds
- Top 10 Regular Seeds
- Top 10 USA Cannabis Strains
-
Favourites
- Beginner Strains
- Below 1% THC
- Classic Cannabis Strains
- Cup Winners
- F1 Hybrids
- Fast Flowering Seeds
- High CBD Strains
- High THC Strains
- Mix Packs
- Zamnesia Exclusive Collabs
-
-
Headshop
-
Vaporshop
- Spare Parts & Accessories
- AirVape XS GO (2021)
- Arizer Air MAX
- Arizer Extreme Q
- Arizer Solo 2
- Arizer V-Tower
- Arizer XQ2
- Boundless CFC 2.0 Vaporizer
- Boundless CFX
- Boundless TERA (V3)
- CRAFTY+
- DaVinci IQC
- Dr. Dabber Boost EVO
- DynaVap VapCap "M" PLUS 2023
- DynaVap VonG (i) Titanium
- Flowermate Aura
- Flowermate Cap Pro
- Flowermate Slick
- Flowermate V5.0S Pro
-
Healthshop
-
Smartshop
-
Shroomshop
-
Growshop
-
Seedshop
All CategoriesSeedshop
- Autoflower Seeds
- Feminized Cannabis Seeds
- Zamnesia Seeds
- Zamnesia's Top 10
- CBD Seeds
- F1 Hybrids
- Seed Banks
- Mix Packs
-
Popular Strain Types
- Zamnesia Exclusive Collabs
- Classic Cannabis Strains
- Amnesia Seeds
- Haze Seeds
- Skunk Seeds
- Kush Seeds
- Purple Seeds
- Blueberry Seeds
- Cheese Seeds
- Diesel Seeds
- White Widow Seeds
- Gorilla Seeds
- Northern Lights Seeds
- Granddaddy Purple Seeds
- OG Kush Seeds
- Blue Dream Seeds
- Lemon Haze Seeds
- Bruce Banner Seeds
- Gelato Seeds
- Sour Diesel Seeds
- Jack Herer Seeds
- Girl Scout Cookies Seeds (GSC)
- Wedding Cake Seeds
- Zkittlez Seeds
- Pineapple Express Seeds
- Chemdawg Seeds
- Hindu Kush Seeds
- Mimosa Seeds
- F1 Hybrids
- Mix Packs
- Cup Winners
- Beginner Strains
- High THC Strains
- Fast Flowering Seeds
- Regular Cannabis Seeds
- USA Cannabis Strains
- Cup Winners
- Seedfinder
-
Vaporshop
All CategoriesVaporshop
- Top 10 Vaporizers
- Spare Parts & Accessories
- AirVape XS GO (2021)
- Arizer Air MAX
- Arizer Extreme Q
- Arizer Solo 2
- Arizer V-Tower
- Arizer XQ2
- Boundless CFC 2.0 Vaporizer
- Boundless CFX
- Boundless TERA (V3)
- CRAFTY+
- DaVinci IQC
- Dr. Dabber Boost EVO
- DynaVap VapCap "M" PLUS 2023
- DynaVap VonG (i) Titanium
- Flowermate Aura
- Flowermate Cap Pro
- Flowermate Slick
- Flowermate V5.0S Pro
- G Pen Elite II
- G Pen Micro+
- G Pen Roam
- Hyer Big-E Rig
- MIGHTY+
- PAX Mini
- PAX Plus
- PLENTY
- Puffco Peak Smart Rig
- Puffco Plus
- Storm Vaporizer
- The Proxy (Puffco)
- VOLCANO CLASSIC
- VOLCANO HYBRID
- Vapman 2.0
- Vapman Click
-
Smartshop
All CategoriesSmartshop
- Top 10 Smartshop
- Zamnesia Gift Cards
- After Party
- Aphrodisiacs
- Aromatherapy
- Blue Lotus
- CBD Vape Juice
- Capsule Machines
- Crystals, Gemstones & Minerals
- Dream Herbs
- Drug Tests
- Extracts
- Happy Caps
- Herbal Tea
- Herbs & Seeds
- Incense
- Kanna
- Kratom
- LSA Seeds
- Mescaline Cacti
- Microdosing
- Nootropics
- Relaxing
- Salvia divinorum
- Smart Seeds
- Stimulants
- Supplements
- Tinctures
- Vape Herbs
-
TRIBE
All CategoriesTRIBE
- My Membership
- Spend Gift Points
- TRIBE Sale
- Exclusive products
- Earn Extra Gift Points
-
TRIBE
- Early Access
- Refer a Friend
- Information
-
TRIBE
-
Language
 United States
United States
Wednesday, 18 February and Tuesday, 24 February 2026*
How to use damiana: Everything you need to know

What is damiana, and why are more people talking about it? Discover how this aromatic herb fits into traditional wellness systems and modern self-care. From preparation methods to safety tips, this guide covers everything you need to know before trying it.
Used for centuries in traditional Mexican herbalism, damiana is making a quiet comeback. It’s best known for helping with tension and libido, and for supporting general well-being. But how exactly should you use it? From brewing it as a tea to taking it in capsules or tinctures, there are several ways to add damiana to your routine.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to use damiana safely and effectively. We’ll explain its traditional and modern uses, potential health benefits, dosage guidelines, and possible side effects. You’ll also find out whether you can vape or smoke it, what form works best for different goals, and what to know before buying it.
Whether you’re curious about damiana tea, interested in its aphrodisiac properties, or just want to know the safest dose, this guide covers everything you need to get started.
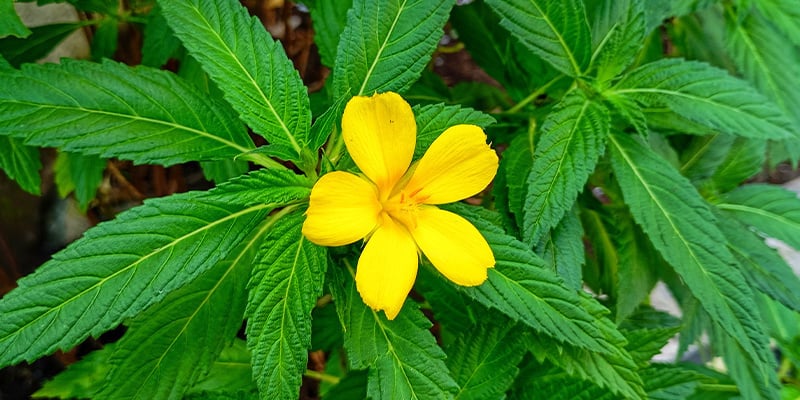
What is damiana?
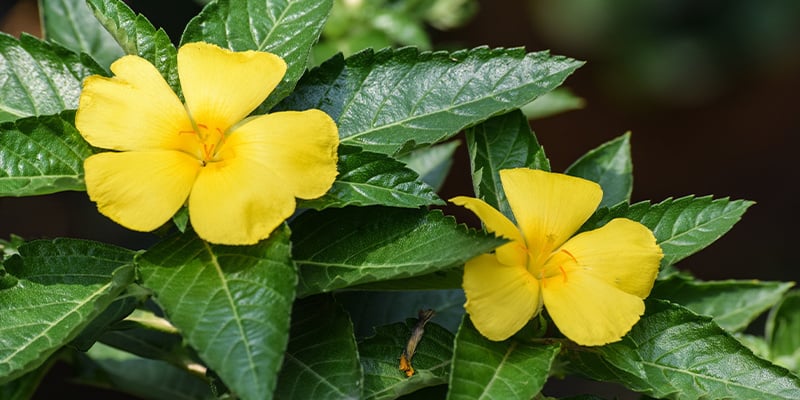

Damiana (Turnera diffusa) is a small shrub with yellow flowers and aromatic leaves. It grows in Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean. The plant has been used in folk holistic practices for generations and remains popular today, especially for its relaxing and libido-boosting effects.
Damiana’s active compounds include flavonoids, tannins, and volatile oils. These may influence the nervous system and hormone activity, though more research is needed to fully understand how it works.
Traditionally, damiana was made into tea or smoked for various purposes. Today, it's available in many forms—tea blends, tinctures, extracts, and capsules. It's commonly used for its soothing properties and to support mood, digestion, and sexual health.
A brief history of damiana
Damiana has been part of indigenous healing practices for hundreds of years. The Maya and Aztecs used it as a tonic, especially to enhance sexual function and treat feelings of stress or low energy. Spanish missionaries first recorded its use in the 1600s.
Today, it’s still used across Mexico and beyond, often in herbal mixtures aimed at boosting mood or libido. Its long history of use continues to influence modern herbal medicine and wellness trends.
Ways to use damiana

There are several ways to use damiana, depending on what you’re hoping to achieve. Some prefer brewing it as a tea, while others use tinctures or capsules for greater ease and more pronounced effects. Damiana can also be smoked or vaped, although this comes with unique risks.
Also, the form you choose may affect how quickly you notice its effects. For example, inhalation tends to act faster than teas or capsules.
Below, we’ll look at each method in more detail, along with preparation tips and dosage guidance.
Damiana tea
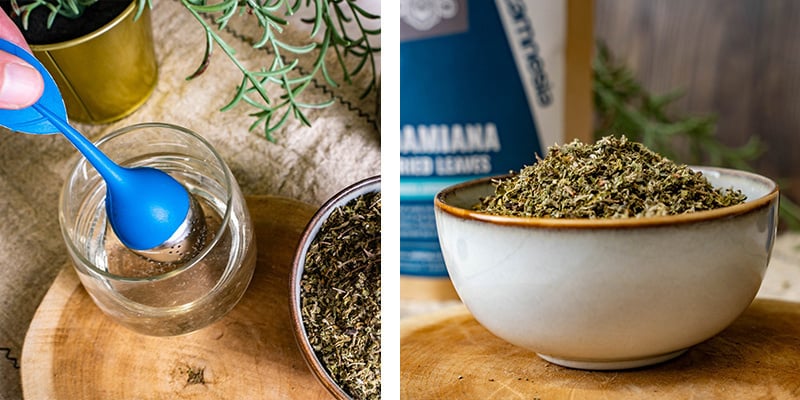

Brewing damiana tea is one of the most traditional and accessible ways to use it. Its flavour is earthy and subtle, often described as soothing. Tea allows the active compounds to be absorbed gradually through the digestive system.
How to make damiana tea:
- Add 1 gram (about ¼ teaspoon) of dried damiana leaves to a cup (250 ml) of hot water
- Steep for 10–15 minutes
- Strain before drinking
You can drink it plain or add honey, lemon, or a cinnamon stick to improve the flavour. It can also be blended with other herbs like passionflower or lemon balm for a tastier and more soothing concoction.
Recommended dosage and frequency:
- 1–3 cups (250–750 ml) per day
- Best taken in the evening if you're using it for relaxation or sleep
Too much tea can lead to mild side effects like upset stomach or insomnia in some people, so it’s best to start small.
Smoking or vaping damiana
Damiana can also be smoked, either on its own or mixed with other herbs. People often report gentle euphoria and a mild body sensation. However, any type of smoke inhalation can be harmful to lung health over time.
Damiana smoking effects:
- May produce mild, short-lived relaxation
- Often used as a tobacco substitute in herbal blends
- Some users report lightheadedness or increased sensitivity
Can you vape damiana?
Yes, you can vape dried damiana leaves using a dry herb vaporizer. Set the temperature to 175–190°C. Vaping might reduce some of the risks linked to smoke, but there’s not enough long-term data on its safety to confirm this.
Damiana tinctures and extracts
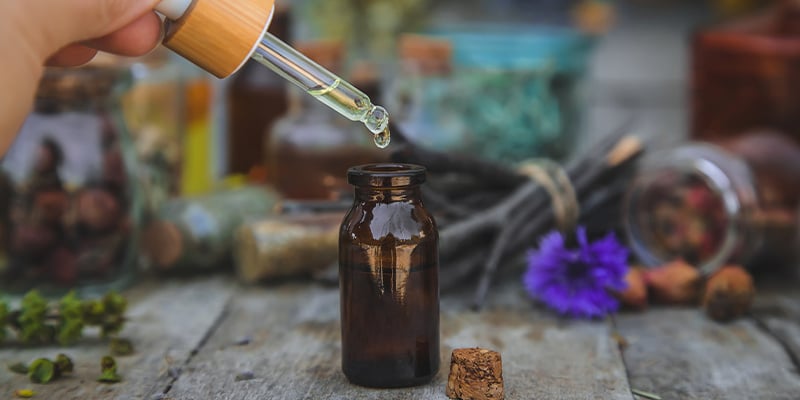

Tinctures are concentrated liquid extracts, often made using alcohol or glycerine. They’re more potent than teas and offer faster absorption, especially for mood support.
How to use damiana extract:
- Start with 2–3 ml (about half a teaspoon)
- Can be taken up to three times a day
- Drop under the tongue or dilute in a small amount of water
Because tinctures are stronger, they’re often preferred when you want more noticeable or immediate effects. Be cautious with dosing to avoid potential side effects.
Damiana supplements and capsules
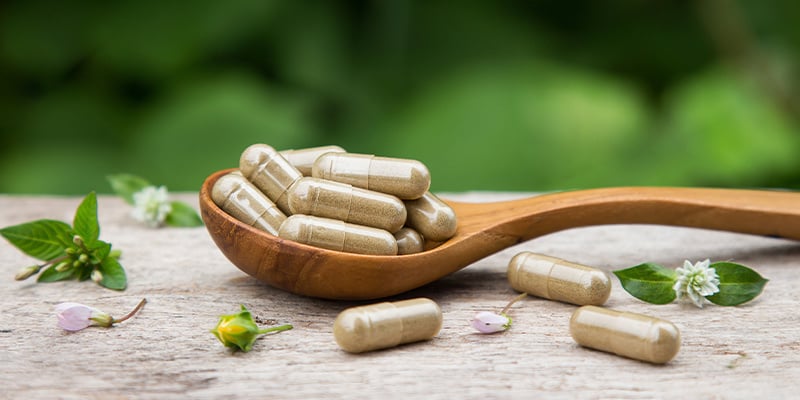

Capsules and tablets are the most convenient option if you want a precise dose without the taste or prep work. They’re also easier to include in a daily routine.
Common over-the-counter forms contain:
- 400–800 mg damiana extract per capsule
- Often combined with other herbs in libido or mood formulas
How they compare to other forms:
- Longer to take effect than tinctures
- No flavour or scent, which some users prefer
- Useful for consistent dosing over time
Look for standardised extracts from trusted brands to ensure quality and potency.
Wellness benefits of damiana

As referenced, damiana has been used for centuries for its effects on sexual health, mood, and digestion. Most of the evidence is historical or anecdotal, though early research does support some of its traditional uses. While it’s not a replacement for medical treatment, it may offer mild benefits for general well-being.
Libido and aphrodisiac effects
Damiana is most widely known as a natural aphrodisiac. The Maya and Aztecs used it to stimulate sexual desire and improve performance. This reputation still holds today, and many modern supplements for sexual health include damiana as a key ingredient.
How it might work:
- It may support blood flow to sexual organs
- It could influence hormone activity or neurotransmitters linked to arousal
- Some report stronger orgasms and increased libido after regular use
A 2013 study on herbal combinations for sexual function found that damiana, among other herbs, improved sexual satisfaction in women (Estrada-Reyes et al.). However, more research is needed to isolate its specific effects.
Mood enhancement

Damiana is sometimes used to support emotional well-being, especially in times of stress or anxiety. It’s thought to have mild nervine effects, meaning it may help ease the nervous system.
Potential effects on mood:
- Promotes a relaxed, balanced state
- May ease mental tension
- Can be taken daily in moderate amounts
Preclinical studies suggest that damiana may act on the nervous system, which may in turn affect anxiety (Paladini et al., 1999). However, clinical trials are limited.
Other benefits
In traditional use, damiana has been applied for various physical complaints, especially those affecting the gut and urinary system.
Reported uses include:
- Soothing mild stomach upset or bloating
- Supporting urinary tract health
- Easing menstrual cramps
Again, most of these claims are based on folk use rather than hard scientific evidence. Still, some people find it helpful as a gentle tonic.
Damiana dosage and safety guidelines

When used correctly, damiana is generally safe for most adults. However, overuse or certain health conditions can increase the risk of side effects. Always start with a low dose, and check with a healthcare provider if you’re unsure.
General dosage recommendations:
- Tea: 1–3 cups per day, each made with 1 gram of dried leaves
- Tincture: 2–3 ml, up to three times daily
- Capsules: 400–800 mg, taken up to three times daily
Stick to the lower end of the range when starting out. Some people find that even small amounts are enough.
What are the side effects of damiana?
Damiana is well tolerated in moderate amounts, but side effects can appear if you take too much or use it too frequently.
Possible side effects:
- Insomnia
- Headaches
- Mild nausea or digestive upset
- Hallucinations (at extremely high doses—rare but documented)
Interactions and warnings:
- Avoid if you’re pregnant or breastfeeding
- Damiana may interact with diabetes medications, as it can affect blood sugar levels
- Those with liver problems should avoid damiana tinctures made with alcohol
- If you're taking prescription medications, consult your GP or a pharmacist before using damiana
Buying and storing damiana

To get the best results, it’s worth choosing high-quality damiana from a reputable source. You can buy it online or in specialist health shops, either as loose dried leaves, capsules, or tinctures.
Where to buy damiana:
- Online retailers specialising in herbal products
- Organic or health food shops
- Supplement shops with botanical sections
Always check for third-party testing or organic certification where possible.
Storage tips:
- Keep dried leaves in a sealed container, away from heat and sunlight
- Store tinctures in a dark bottle in a cool place
- Capsules should be kept dry and away from direct light
Shelf life:
- Dried leaves: Around 1 year if stored properly
- Tinctures: Up to 2 years
- Capsules: Follow expiry date on the label
Damiana: Frequently asked questions

- Can you use damiana every day?
- Yes, many people use damiana daily. If taken in moderate doses, it’s generally safe. That said, taking breaks now and then is a good idea to reduce the chance of tolerance or side effects.
- How long before effects are noticeable?
- It depends on the form. Tea and tinctures may start working within 30–60 minutes. Capsules may take longer but offer more consistent results with regular use.
- Is damiana legal everywhere?
- Damiana is legal in most countries, including the UK. However, some places restrict its sale or possession due to its mild psychoactive effects when smoked. If unsure, check your local laws.
- What should you not mix with damiana?
- Avoid combining damiana with alcohol or sedatives, medications that affect blood sugar, or other herbs that strongly impact mood or blood pressure. If you’re on medication or have a health condition, get professional medical advice before mixing damiana with anything else.
Try damiana with care and curiosity

Damiana is one of those herbs that’s easy to try and may offer a subtle lift—whether to your mood, your energy, or your sex life. Its long history of use, especially in Mexican folk practices, gives it a trusted place in natural health routines.
You don’t need to overdo it. Start with a cup of tea or a single supplement, see how your body responds, and go from there. With proper use, damiana can be a gentle, natural way to support relaxation and well-being.

- Estrada-Reyes, R., Carro-Juárez, M., & Martínez-Mota, L. (2013/03/07). Pro-sexual effects of Turnera diffusa Wild (Turneraceae) in male rats involves the nitric oxide pathway - https://www.sciencedirect.com
- Paladini, A. C., Marder, M., Viola, H., Wolfman, C., Wasowski, C., & Medina, J. H. (1999). Flavonoids and the central nervous system: from forgotten factors to potent anxiolytic compounds - https://academic.oup.com
- France
- Germany
- International
- Italy
- Netherlands
- Polska
- Portugal
- Spain
- United Kingdom
- United States
Aphrodisiacs
-
€ 8,90 € 6,94+5 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 13,95 € 10,88
-
€ 13,95 € 10,88+7 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 8,95 € 6,98+5 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 19,99 € 13,39+10 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 29,99 € 23,39
-
€ 7,50 € 5,85+4 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 29,50 € 26,26+16 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 9,95 € 7,76+5 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 7,50 € 3,38+4 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 25,99 € 23,13+14 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 5,90 € 4,60+3 Extra Gift Points
-
€ 5,50 € 4,29+3 Extra Gift Points
You might also like
-

 5 min
20 May 2025
Top 7 nootropics to boost mental performance
Nootropics occur in nature and can also be synthesised in labs. But with so many options, finding the right one isn't easy. Discover our 7 top picks to support memory and focus. ...
5 min
20 May 2025
Top 7 nootropics to boost mental performance
Nootropics occur in nature and can also be synthesised in labs. But with so many options, finding the right one isn't easy. Discover our 7 top picks to support memory and focus. ...
-

 4 min
1 June 2023
What Are The Best Drugs To Have Sex On?
Sex and drugs have been used together for ages. Some drugs can enhance sex. Others, however, are highly dangerous and should be avoided. We take a look at the good, the bad, and the ugly. ...
4 min
1 June 2023
What Are The Best Drugs To Have Sex On?
Sex and drugs have been used together for ages. Some drugs can enhance sex. Others, however, are highly dangerous and should be avoided. We take a look at the good, the bad, and the ugly. ...
-

 4 min
19 August 2022
7 Natural Aphrodisiacs For Women
Sometimes our sex drive needs a little boost. And if we can do so using natural substances, that's all the better. Here we look at 7 natural aphrodisiacs that may help women to increase their libidos. ...
4 min
19 August 2022
7 Natural Aphrodisiacs For Women
Sometimes our sex drive needs a little boost. And if we can do so using natural substances, that's all the better. Here we look at 7 natural aphrodisiacs that may help women to increase their libidos. ...
-

 2 min
14 August 2017
How To Use Damiana To Increase Your Libido And Enhance Orgasms
Used for centuries as an aphrodisiac, Damiana is an effective supplement to boost libido. The plant demonstrates an ability to potentially boost sexual desire and intensify orgasms in men and women. ...
2 min
14 August 2017
How To Use Damiana To Increase Your Libido And Enhance Orgasms
Used for centuries as an aphrodisiac, Damiana is an effective supplement to boost libido. The plant demonstrates an ability to potentially boost sexual desire and intensify orgasms in men and women. ...
Categories
-
Seedshop
- Feminized Cannabis Seeds
- Autoflower Seeds
- Regular Cannabis Seeds
- F1 Hybrids
- CBD Seeds
- Zamnesia Seeds
- Top 10 Autoflowering Seeds
- Top 10 Regular Seeds
- Top 10 USA Cannabis Strains
- Top 10 Feminized Seeds
- Beginner Strains
- Below 1% THC
- Classic Cannabis Strains
- Cup Winners
- F1 Hybrids
- Fast Flowering Seeds
- High CBD Strains
- High THC Strains
- Mix Packs
- Zamnesia Exclusive Collabs
- Amnesia Seeds
- Blueberry Seeds
- Cheese Seeds
- Diesel Seeds
- Gorilla Seeds
- Haze Seeds
- Kush Seeds
- Purple Seeds
- Skunk Seeds
- White Widow Seeds
- Northern Lights Seeds
- Granddaddy Purple Seeds
- OG Kush Seeds
- Blue Dream Seeds
- Lemon Haze Seeds
- Bruce Banner Seeds
- Gelato Seeds
- Sour Diesel Seeds
- Jack Herer Seeds
- Girl Scout Cookies Seeds (GSC)
- Wedding Cake Seeds
- Zkittlez Seeds
- Pineapple Express Seeds
- Chemdawg Seeds
- Hindu Kush Seeds
- Mimosa Seeds
- Zamnesia Seeds
- ACE Seeds
- Advanced Seeds
- Afghan Seed Connection
- Amsterdam Genetics
- Anesia Seeds
- Auto Seeds
- Barney's Farm
- Big Buddha Seeds
- Blimburn Seeds
- Bomb Seeds
- BSB Genetics
- BSF Seeds
- Buddha Seeds
- The Cali Connection Seeds
- CBD Seeds
- Compound Genetics
- Cookies Seed Bank
- Delicious Seeds
- DNA Genetics
- Doctor's Choice
- Dr. Underground
- Dutch Passion
- Elite Seeds
- Eva Seeds
- Exotic Seed
- Expert Seeds
- FastBuds
- Female Seeds
- French Touch Seeds
- Garden of Green
- GeneSeeds
- Genehtik Seeds
- G13 Labs
- Grass-O-Matic
- Greenhouse Seeds
- Growers Choice
- Humboldt Seed Company
- Humboldt Seed Organization
- Kalashnikov Seeds
- Kannabia
- The Kush Brothers
- Light Buds
- Little Chief Collabs
- Medical Seeds
- Ministry of Cannabis
- Mr. Nice
- Nirvana Seeds
- Original Sensible
- Paradise Seeds
- Perfect Tree
- Pheno Finder
- Philosopher Seeds
- Positronics Seeds
- Purple City Genetics
- Pyramid Seeds
- Rare Dankness
- Reggae Seeds
- Resin Seeds
- Ripper Seeds
- Royal Queen Seeds
- Sagarmatha Seeds
- Samsara Seeds
- Seedstockers
- Sensation Seeds
- Sensi Seeds
- Serious Seeds
- Silent Seeds
- Solfire Gardens
- Soma Seeds
- Spliff Seeds
- Strain Hunters
- Sumo Seeds
- Super Sativa Seed Club
- Super Strains
- Sweet Seeds
- TICAL
- T.H. Seeds
- Top Tao Seeds
- Vision Seeds
- VIP Seeds
- White Label
- World Of Seeds
- Seed Banks
-
Headshop
-
Vaporshop
-
Healthshop
-
Smartshop
- Top 10 Smartshop
- Kratom Dosage Calculator
- Zamnesia Gift Cards
- After Party
- Aphrodisiacs
- Aromatherapy
- Blue Lotus
- CBD Vape Juice
- Capsule Machines
- Crystals, Gemstones & Minerals
- Dream Herbs
- Drug Tests
- Extracts
- Happy Caps
- Herbal Tea
- Herbs & Seeds
- Incense
- Kanna
- Kratom
- LSA Seeds
- Mescaline Cacti
- Microdosing
- Nootropics
- Relaxing
- Salvia divinorum
- Smart Seeds
- Stimulants
- Supplements
- Tinctures
- Vape Herbs
-
Shroomshop
-
Growshop
- Top 10 Growshop
- Top 10 Plant Seeds
- All Seeds
- Cacti
- Chili & Pepper Seeds
- Companion Plants
- Edible Plant Seeds
- Exotic Seeds
- Flower Seeds
- Fruit Seeds
- Herb Seeds
- Interior Plant Seeds
- Microgreens
- Psychoactive Plant Seeds
- Sprouting
- Vegetable Seeds
- Wellness Plant Seeds
- After Harvest
- Climate Control
- Fertilizer
- Grow Tents
- Harvest, Dry & Cure
- LED Grow Lights
- Plant Seeds
- Propagation
-
Merchandise
-
Sale section
Categories
Discover
Help & Info
Tools
Our website won't work without these cookies activated. Therefore functional cookies can't be disabled.