-
Seedshop
-
Feminized
Cannabis seeds -
Autoflowering
Cannabis Seeds -
Regular
Cannabis Seeds -
F1 Hybrid
Cannabis Seeds -
CBD
Cannabis Seeds -
Zamnesia
Cannabis Seeds
-
Top 10’s
- Top 10 Feminized Seeds
- Top 10 Autoflowering Seeds
- Top 10 Regular Seeds
- Top 10 USA Cannabis Strains
-
Favourites
- Beginner Strains
- Below 1% THC
- Classic Cannabis Strains
- Cup Winners
- F1 Hybrids
- Fast Flowering Seeds
- High CBD Strains
- High THC Strains
- Mix Packs
- Zamnesia Exclusive Collabs
- Zamnesia Experimental
-
-
Headshop
-
Vaporshop
- Spare Parts & Accessories
- AirVape XS GO (2021)
- Arizer Air MAX
- Arizer Extreme Q
- Arizer Solo 2
- Arizer V-Tower
- Arizer XQ2
- Boundless CFC 2.0 Vaporizer
- Boundless CFX
- Boundless TERA (V3)
- CRAFTY+
- DaVinci IQC
- Dr. Dabber Boost EVO
- DynaVap VapCap "M" PLUS 2023
- DynaVap VonG (i) Titanium
- Flowermate Aura
- Flowermate Cap Pro
- Flowermate Slick
- Flowermate V5.0S Pro
-
Healthshop
-
Smartshop
-
Shroomshop
-
Growshop
-
Seedshop
All CategoriesSeedshop
- Autoflower Seeds
- Feminized Cannabis Seeds
- Zamnesia Seeds
- Zamnesia's Top 10
- CBD Seeds
- F1 Hybrids
- Seed Banks
- Mix Packs
-
Popular Strain Types
- Zamnesia Exclusive Collabs
- Classic Cannabis Strains
- Amnesia Seeds
- Haze Seeds
- Skunk Seeds
- Kush Seeds
- Purple Seeds
- Blueberry Seeds
- Cheese Seeds
- Diesel Seeds
- White Widow Seeds
- Gorilla Seeds
- Northern Lights Seeds
- Granddaddy Purple Seeds
- OG Kush Seeds
- Blue Dream Seeds
- Lemon Haze Seeds
- Bruce Banner Seeds
- Gelato Seeds
- Sour Diesel Seeds
- Jack Herer Seeds
- Girl Scout Cookies Seeds (GSC)
- Wedding Cake Seeds
- Zkittlez Seeds
- Pineapple Express Seeds
- Chemdawg Seeds
- Hindu Kush Seeds
- Mimosa Seeds
- F1 Hybrids
- Mix Packs
- Cup Winners
- Beginner Strains
- High THC Strains
- Fast Flowering Seeds
- Regular Cannabis Seeds
- USA Cannabis Strains
- Cup Winners
- Seedfinder
- Zamnesia Experimental
-
Vaporshop
All CategoriesVaporshop
- Top 10 Vaporizers
- Spare Parts & Accessories
- AirVape XS GO (2021)
- Arizer Air MAX
- Arizer Extreme Q
- Arizer Solo 2
- Arizer V-Tower
- Arizer XQ2
- Boundless CFC 2.0 Vaporizer
- Boundless CFX
- Boundless TERA (V3)
- CRAFTY+
- DaVinci IQC
- Dr. Dabber Boost EVO
- DynaVap VapCap "M" PLUS 2023
- DynaVap VonG (i) Titanium
- Flowermate Aura
- Flowermate Cap Pro
- Flowermate Slick
- Flowermate V5.0S Pro
- G Pen Elite II
- G Pen Micro+
- G Pen Roam
- Hyer Big-E Rig
- MIGHTY+
- PAX Mini
- PAX Plus
- PLENTY
- Puffco Peak Smart Rig
- Puffco Plus
- Storm Vaporizer
- The Proxy (Puffco)
- VOLCANO CLASSIC
- VOLCANO HYBRID
- Vapman 2.0
- Vapman Click
-
Smartshop
All CategoriesSmartshop
- Top 10 Smartshop
- Zamnesia Gift Cards
- After Party
- Aphrodisiacs
- Aromatherapy
- Blue Lotus
- CBD Vape Juice
- Capsule Machines
- Crystals, Gemstones & Minerals
- Dream Herbs
- Drug Tests
- Extracts
- Happy Caps
- Herbal Tea
- Herbs & Seeds
- Incense
- Kanna
- Kratom
- LSA Seeds
- Mescaline Cacti
- Microdosing
- Nootropics
- Relaxing
- Salvia divinorum
- Smart Seeds
- Stimulants
- Supplements
- Tinctures
- Vape Herbs
-
TRIBE
All CategoriesTRIBE
- My Membership
- Spend Gift Points
- TRIBE Sale
- Exclusive products
- Earn Extra Gift Points
-
TRIBE
- Early Access
- Refer a Friend
- Information
-
TRIBE
-
Language
 United States
United States
Thursday, 12 March and Wednesday, 18 March 2026*
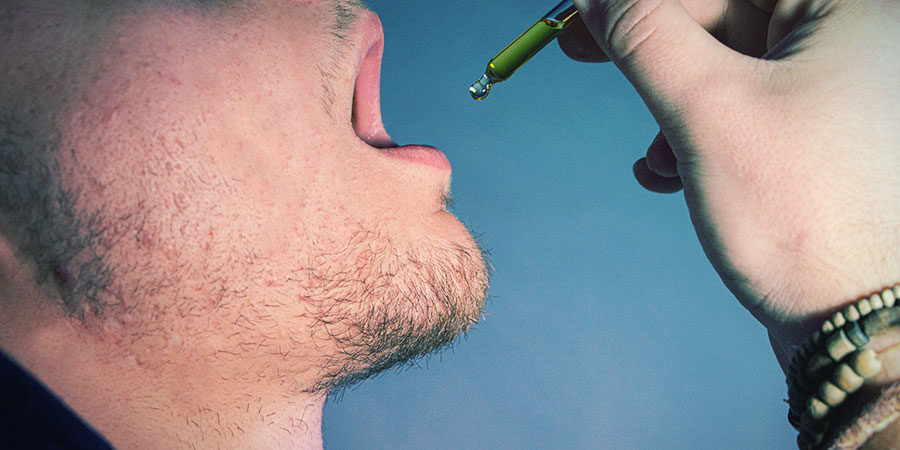
Is It Okay To Mix Alcohol And CBD?
CBD’s recent explosion in popularity has led to its inclusion in a wide variety of different industries ranging from foods to cosmetics. One sector currently gaining steam is the market for CBD-infused alcoholic beverages. But what are the implications?
Infused cocktails can be found in upscale California bars, while Oregon’s cannabis-friendly culture has seen a steady rise in CBD IPAs. Moreover, Canada is set to join the CBD-infused alcohol party in October of 2019.
On a global scale, the trend of breweries partnering with licensed marijuana companies has experts believing that infused drinks will soon become a big part of the legal marijuana market.
However, even if you consume CBD and alcohol separately, you can still expect them to interact. In fact, it is believed that even if consumed several hours apart, these substances will still affect one another.
HOW DOES ALCOHOL AFFECT THE HUMAN BODY?
When alcohol is ingested, roughly 20% of it enters the bloodstream immediately through the stomach, while the other 80% is absorbed through the small intestines. Once it enters the bloodstream, it is transported to the liver for processing and metabolisation.
Alcohol has numerous effects on the brain and body in both the short and long-term. In the short-term, alcohol tends to cause cognitive impairment, poor judgment, loss of coordination, trouble concentrating, and mood swings. It can also cause visual impairment, high blood pressure, and nausea. In the long-run, alcohol can cause chronic issues such as memory loss, depression, learning problems, and liver fibrosis.
HOW DOES CBD AFFECT THE HUMAN BODY?
After it is consumed, CBD is processed by a regulatory system called the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is a network of cell receptors throughout the body that interact with cannabinoids and enzymes to produce effects. Researchers believe that the ECS is responsible for regulating homeostasis (internal equilibrium).
Although CBD doesn’t have a high affinity for the ECS’ two main receptors, research shows that it interacts directly and indirectly with several other kinds of cell receptors. These include 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine), PPAR receptors (peroxisome proliferator-activated), and TRPV1 receptors (transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1), among others.
Clinical and animal studies show that CBD may have a range of applications. However, because CBD works via such a complex physiological network, and because everyone is different, the strength of its effects may also differ from person to person.
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN ALCOHOL AND CBD ARE MIXED?

Cannabis and alcohol are both depressants, and consuming them at the same time will most likely amplify their effects. Depressant drugs affect the central nervous system. When consumed in small doses, the CBD induces stimulating effects. However, when consumed in large doses, CBD also exhibits relaxing properties.
A clinical study (Consroe et al., 1979) from 1979 dosed human test subjects with both alcohol and a combination of alcohol and CBD. Researchers detected “few differences” between the two groups in terms of inebriation or impairment, with both groups showing a significantly reduced ability to function. Interestingly, researchers found that test subjects who also consumed CBD had lower blood alcohol levels than those who consumed just alcohol. This indicates that CBD may have some role to play in the management of blood alcohol level.
However, anecdotal evidence suggests that consuming both cannabidiol and alcohol at the same time amplifies the relaxing effects of each. As your level of intoxication grows, you can also expect a greater loss of inhibition and motor coordination.
ARE THERE ANY ADVANTAGES TO MIXING ALCOHOL AND CBD?

Some evidence exists to suggest that CBD may actually have some beneficial effects related to the consumption of alcohol.
If nothing more, taking CBD after drinking may improve your hangover symptoms (Parker et al., 2011). Because alcohol and cannabidiol appear relatively safe to mix together, taking a dose of CBD near the end of your drinking session may give you a head start on that hangover.

- Consroe P, Carlini EA, Zwicker AP, & Lacerda LA. (1979). Interaction of cannabidiol and alcohol in humans - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Linda A Parker, Erin M Rock, & Cheryl L Limebeer. (2011, August). Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- France
- Germany
- International
- Italy
- Netherlands
- Polska
- Portugal
- Spain
- United Kingdom
- United States
You might also like
-

 5 min
26 January 2026
CBD oil: Your ultimate guide
A clear, evidence-minded guide for beginners and regular users. Learn CBD extract types, strength, and dosing basics, how to read labels and lab reports, and tips for choosing the right product. Inclu ...
5 min
26 January 2026
CBD oil: Your ultimate guide
A clear, evidence-minded guide for beginners and regular users. Learn CBD extract types, strength, and dosing basics, how to read labels and lab reports, and tips for choosing the right product. Inclu ...
-

 6 min
9 August 2022
What Is Cannabidiol (CBD)?
CBD has risen to stardom in the supplement world. But what propelled a single plant-derived molecule to such great heights? There are certain elements at play here. Early research has turned out some ...
6 min
9 August 2022
What Is Cannabidiol (CBD)?
CBD has risen to stardom in the supplement world. But what propelled a single plant-derived molecule to such great heights? There are certain elements at play here. Early research has turned out some ...
-

 3 min
9 November 2019
Full Spectrum CBD Vs. CBD Isolate: Which Is Better?
With an array of different CBD products on the market, questions inevitably arise about their comparative effectiveness. When it comes to full spectrum CBD versus CBD isolate, the main difference is c ...
3 min
9 November 2019
Full Spectrum CBD Vs. CBD Isolate: Which Is Better?
With an array of different CBD products on the market, questions inevitably arise about their comparative effectiveness. When it comes to full spectrum CBD versus CBD isolate, the main difference is c ...
-

 2 min
12 November 2018
The Difference Between CBD Oil And Rick Simpson Oil
Thanks to the highly successful documentary Run From The Cure, the Rick Simpson oil became a household name almost over night. We'll explain the difference between CBD oil and Rick Simpson oil. ...
2 min
12 November 2018
The Difference Between CBD Oil And Rick Simpson Oil
Thanks to the highly successful documentary Run From The Cure, the Rick Simpson oil became a household name almost over night. We'll explain the difference between CBD oil and Rick Simpson oil. ...
Categories
-
Seedshop
- Feminized Cannabis Seeds
- Autoflower Seeds
- Regular Cannabis Seeds
- F1 Hybrids
- CBD Seeds
- Zamnesia Seeds
- Top 10 Autoflowering Seeds
- Top 10 Regular Seeds
- Top 10 USA Cannabis Strains
- Top 10 Feminized Seeds
- Beginner Strains
- Below 1% THC
- Classic Cannabis Strains
- Cup Winners
- F1 Hybrids
- Fast Flowering Seeds
- High CBD Strains
- High THC Strains
- Mix Packs
- Zamnesia Exclusive Collabs
- Zamnesia Experimental
- Amnesia Seeds
- Blueberry Seeds
- Cheese Seeds
- Diesel Seeds
- Gorilla Seeds
- Haze Seeds
- Kush Seeds
- Purple Seeds
- Skunk Seeds
- White Widow Seeds
- Northern Lights Seeds
- Granddaddy Purple Seeds
- OG Kush Seeds
- Blue Dream Seeds
- Lemon Haze Seeds
- Bruce Banner Seeds
- Gelato Seeds
- Sour Diesel Seeds
- Jack Herer Seeds
- Girl Scout Cookies Seeds (GSC)
- Wedding Cake Seeds
- Zkittlez Seeds
- Pineapple Express Seeds
- Chemdawg Seeds
- Hindu Kush Seeds
- Mimosa Seeds
- Zamnesia Seeds
- ACE Seeds
- Advanced Seeds
- Afghan Seed Connection
- Amsterdam Genetics
- Anesia Seeds
- Auto Seeds
- Barney's Farm
- Big Buddha Seeds
- Blimburn Seeds
- Bomb Seeds
- BSB Genetics
- BSF Seeds
- Buddha Seeds
- The Cali Connection Seeds
- CBD Seeds
- Compound Genetics
- Cookies Seed Bank
- Delicious Seeds
- DNA Genetics
- Doctor's Choice
- Dr. Underground
- Dutch Passion
- Elite Seeds
- Eva Seeds
- Exotic Seed
- Expert Seeds
- FastBuds
- Female Seeds
- French Touch Seeds
- Garden of Green
- GeneSeeds
- Genehtik Seeds
- G13 Labs
- Grass-O-Matic
- Greenhouse Seeds
- Growers Choice
- Humboldt Seed Company
- Humboldt Seed Organization
- Kalashnikov Seeds
- Kannabia
- The Kush Brothers
- Light Buds
- Little Chief Collabs
- Medical Seeds
- Ministry of Cannabis
- Mr. Nice
- Nirvana Seeds
- Original Sensible
- Paradise Seeds
- Perfect Tree
- Pheno Finder
- Philosopher Seeds
- Positronics Seeds
- Purple City Genetics
- Pyramid Seeds
- Rare Dankness
- Reggae Seeds
- Resin Seeds
- Ripper Seeds
- Royal Queen Seeds
- Sagarmatha Seeds
- Samsara Seeds
- Seedstockers
- Sensation Seeds
- Sensi Seeds
- Serious Seeds
- Silent Seeds
- Solfire Gardens
- Soma Seeds
- Spliff Seeds
- Strain Hunters
- Sumo Seeds
- Super Sativa Seed Club
- Super Strains
- Sweet Seeds
- TICAL
- T.H. Seeds
- Top Tao Seeds
- Vision Seeds
- VIP Seeds
- White Label
- World Of Seeds
- Seed Banks
-
Headshop
-
Vaporshop
-
Healthshop
-
Smartshop
- Top 10 Smartshop
- Kratom Dosage Calculator
- Zamnesia Gift Cards
- After Party
- Aphrodisiacs
- Aromatherapy
- Blue Lotus
- CBD Vape Juice
- Capsule Machines
- Crystals, Gemstones & Minerals
- Dream Herbs
- Drug Tests
- Extracts
- Happy Caps
- Herbal Tea
- Herbs & Seeds
- Incense
- Kanna
- Kratom
- LSA Seeds
- Mescaline Cacti
- Microdosing
- Nootropics
- Relaxing
- Salvia divinorum
- Smart Seeds
- Stimulants
- Supplements
- Tinctures
- Vape Herbs
-
Shroomshop
-
Growshop
- Top 10 Growshop
- Top 10 Plant Seeds
- All Seeds
- Cacti
- Chili & Pepper Seeds
- Companion Plants
- Edible Plant Seeds
- Exotic Seeds
- Flower Seeds
- Fruit Seeds
- Herb Seeds
- Interior Plant Seeds
- Microgreens
- Psychoactive Plant Seeds
- Sprouting
- Vegetable Seeds
- Wellness Plant Seeds
- After Harvest
- Climate Control
- Fertilizer
- Grow Tents
- Harvest, Dry & Cure
- LED Grow Lights
- Plant Seeds
- Propagation
-
Merchandise
-
Sale section
Categories
Discover
Help & Info
Tools
Our website won't work without these cookies activated. Therefore functional cookies can't be disabled.