
What Is Pinene In Cannabis?
Heard about pinene and its potential effects in humans? Keep reading for a detailed overview of pinene, one of the most common chemical compounds found in cannabis. Find out what it smells like, which plants feature it in abundance, and its potential as a wellness agent.
Cannabis contains hundreds of compounds, including terpenes; volatile aromatic chemicals that not only affect the smell of this ancient plant, but also its effects on the human body. In this article, we take a closer look at pinene, one of the most common terpenes found in cannabis, which boasts a unique "fresh pine" aroma and a wide variety of potential effects.
What is pinene?

Pinene is one of the most prominent terpenes found in nature. It exists in two variants—α-pinene and β-pinene—and is one of the most well-researched terpenes to date. Pinene is also one of the most abundant terpenes in cannabis, but it can also be found in many other natural sources, like those listed below. In fact, pinene is commonly found in many essential oils, sometimes in concentrations up to or exceeding 10%, which is very high when compared to other terpenes.
Where can you find pinene?
Pinene is one of the main compounds in cannabis, but it can be found in many other plants as well. These include:
- Pine needles (and liquid extracts made from conifers)
- Rosemary
- Basil
- Thyme
- Dill
- Eucalyptus
- Camphorweed
- Sagebrush
- Cedar
- Citrus peels
What does pinene smell like?

As its name suggests, pinene has a distinct aroma associated with the clean, fresh smell of pine trees. The aroma of pinene is also earthy and somewhat musky; think of the aroma of a Christmas tree, conifers, or the invigoratingly fresh smell of a large, open pine forest. Pinene also has herbal undertones similar to those that you'd find in the aromas of fresh basil, thyme, and dill, as well some woody notes reminiscent of spruce, fir, and cedar.
Some words to help you imagine the aroma of pinene include:
- Resinous
- Weedy
- Leathery
- Spicy
- Herbal
- Balsamic
What is the chemical structure of pinene?
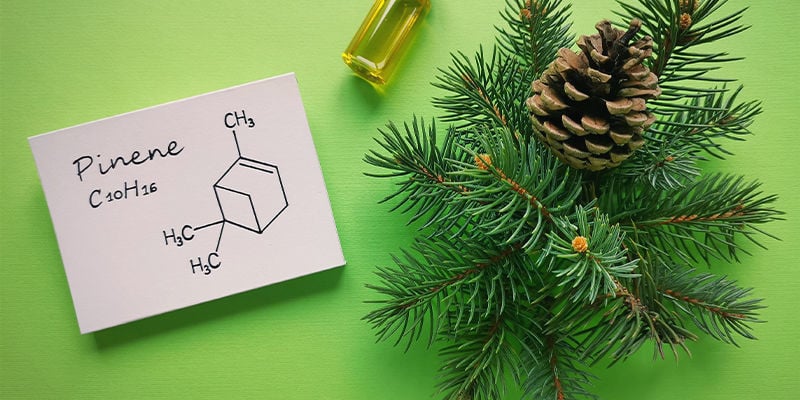
α-pinene is a bicyclic monoterpene, meaning its chemical structure is characterised by having two rings (known as enantiomers); one with a positive charge (+) and the other with a negative charge (-). These rings are 3D mirror images of one another and are completely identical. Moreover, α-pinene has a double bond, and its central structure looks somewhat similar to a cube.
β-pinene, a separate terpene in the pinene family, boasts a seemingly similar chemical structure, but with important differences. α-pinene is soluble in both ethanol and oil and has a boiling point of 155°C, whereas β-pinene is soluble only in oil and has a slightly higher boiling point of 163–166°C.
What are the potential benefits of pinene?

Pinene has been the focus of many different studies, and is arguably the most well-researched of all cannabis terpenes. Nonetheless, there is still a lot we have to learn about pinene and its potential benefits. So far, studies have investigated pinene's effects on (Salehi et al., 2019):
-
Inflammation: Studies have observed pinene's effects on some inflammatory pathways.
-
Bacteria and fungi: Research has also examined pinene's effect on different microbial life forms, like fungi and bacteria.
-
Tumour growth: Like many other cannabis compounds, pinene has been studied for its effects on tumour growth and cell death.
-
Free radicals and oxidants: Numerous studies have looked into the potential antioxidant properties of pinene and other terpenes.
-
Gastrointestinal health: Research has observed pinene’s impact on gastrointestinal issues such as ulcers and pancreatitis.
-
The nervous system: Some research has been conducted on pinene's effect on neurological pathways and signalling.
For a more detailed and first-hand look at the scientific research into both α- and β-pinene, consider reading a 2019 review by Salehi et al. (listed in the references below this article). Unfortunately, while cannabis research has grown exponentially in recent years, there's still a lot we don't know about this complex plant and its many active compounds. The aforementioned review, however, collects and examines many of the scattered pieces of research on pinene to help paint a more comprehensive picture of the compound's potential benefits.
5 cannabis strains rich in pinene
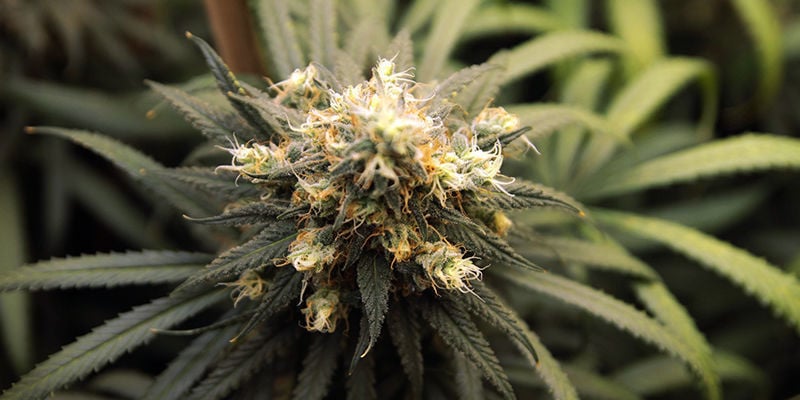

If you're looking for cannabis strains rich in pinene, you're in luck; pinene is one of the most common terps found in a variety of sought-after cannabis cultivars, including the following.
1. Blue Dream
Blue Dream is a treasured US hybrid. A sativa-dominant Haze and Blueberry cross, Blue Dream is loved for its extremely well-balanced effects that activate the mind while relaxing the body. It boasts a delicious sweet berry aroma with subtle underlying hints of earth and fruit.
2. Jack Herer
Jack Herer is a well-known and beloved sativa strain named after the iconic author and cannabis activist. It boasts uplifting, positive effects that kickstart a clear-headed, creative, cerebral buzz. Its highly resinous buds have a mouth-watering citrus scent with a fresh pine kick.
3. OG Kush
OG Kush is a classic strain that was bred in Florida in the 90s and went on to become a household name among cannabis users. Believed to be a mix of Chemdawg, Lemon Thai, and Pakistani Hindu Kush, this potent hybrid boasts a complex aroma that combines the smell of dank fuel with that of spicy Skunk and fresh lemon zest.
4. Cannatonic
Don't forget that CBD strains can be just as rich in terpenes and resin as THC varieties, and Cannatonic is the perfect example of that. Boasting soothing effects without the intoxicating high of THC, Cannatonic also has a strong earthy aroma with an underlying citrus bite.
5. Strawberry Cough
Named for its unique aroma and strength that'll make even the most seasoned smokers cough out hard, Strawberry Cough is a dank hybrid that produces an invigorating and energising high. Her aroma is reminiscent of fresh, sweet, and slightly acidic strawberries and forest berries.
Pinene: A summary
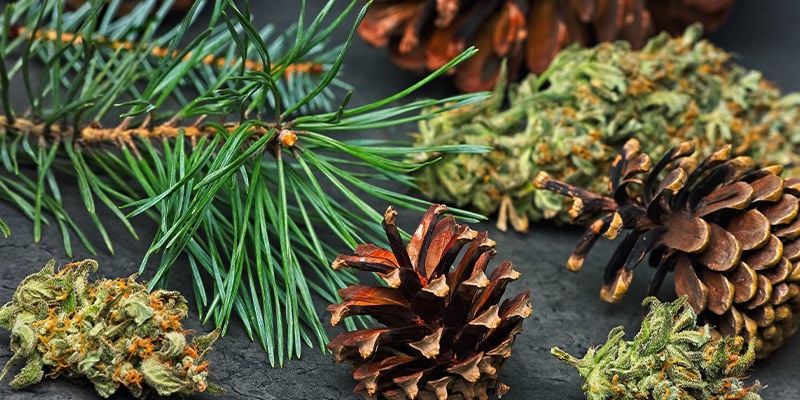

Pinene exists in two distinct variants, which together make up a large share of the terpenes found in nature, and in cannabis specifically. For this reason, pinene has been the focus of a relatively large body of research. While it shows a lot of promise in early studies, more research is needed in order to make concrete conclusions about pinene’s pharmacological impact.
- Bahare Salehi, Shashi Upadhyay, Ilkay Erdogan Orhan, Arun Kumar Jugran, Sumali L.D. Jayaweera, Daniel A. Dias, Farukh Sharopov, Yasaman Taheri, Natália Martins, Navid Baghalpour, William C. Cho, & Javad Sharifi-Rad. (2019, November). Therapeutic Potential of α- and β-Pinene: A Miracle Gift of Nature. Biomolecules Nov; 9(11): 738. - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
 3 min
20 October 2022
What Is Humulene In Cannabis?
Cannabis is rich in terpenes, and humulene is one of the most common. Besides its unique, hoppy aroma, research is looking to observe if humulene may have therapeutic potential. Dive in as we...
3 min
20 October 2022
What Is Humulene In Cannabis?
Cannabis is rich in terpenes, and humulene is one of the most common. Besides its unique, hoppy aroma, research is looking to observe if humulene may have therapeutic potential. Dive in as we...
-
 3 min
6 October 2022
What Is Geraniol In Cannabis?
Geraniol occurs throughout nature, and gives off aromatic, floral scents. Found in many strains of cannabis, does it only taste good, or could it have other beneficial properties? Here we...
3 min
6 October 2022
What Is Geraniol In Cannabis?
Geraniol occurs throughout nature, and gives off aromatic, floral scents. Found in many strains of cannabis, does it only taste good, or could it have other beneficial properties? Here we...
-
 5 min
22 January 2021
What Are Flavonoids, Terpenes, And Terpenoids?
Cannabis flowers appear simple to the naked eye. Yet, these sticky green nuggets house a secret, complex world. Not only do they contain over 100 cannabinoids, but they manufacture hundreds of...
5 min
22 January 2021
What Are Flavonoids, Terpenes, And Terpenoids?
Cannabis flowers appear simple to the naked eye. Yet, these sticky green nuggets house a secret, complex world. Not only do they contain over 100 cannabinoids, but they manufacture hundreds of...
-
 4 min
30 May 2018
Everything You Need To Know About Terpenes
If terpenes and terpenoids sound the same to you, that's because, for the most part, they are. But there is a small difference between these two compounds; terpenes are pure hydrocarbons....
4 min
30 May 2018
Everything You Need To Know About Terpenes
If terpenes and terpenoids sound the same to you, that's because, for the most part, they are. But there is a small difference between these two compounds; terpenes are pure hydrocarbons....







 United States
United States











