Phosphorus deficiency in cannabis plants: Symptoms & fixes

Phosphorus is crucial for cannabis root growth and bud development. Learn to spot, treat, and prevent deficiencies to keep your plants thriving from seed to harvest, with tools and tips to grow better.
Even the most well-intentioned, patient, and attentive growers can find their plants struggling; leaves curling, stems darkening, buds failing to bulk up. Often, the culprit isn't pests or poor genetics, but something far subtler: a nutrient imbalance.
Among the most overlooked yet essential elements is phosphorus, a macronutrient that is critical in root development, bud production, and the plant's overall vitality. Left unchecked, phosphorus deficiency in cannabis can silently stunt growth and reduce yields, especially during flowering.
In this guide, we'll show you how to spot the signs early, fix the problem fast, and prevent it from sabotaging your harvest.
Why phosphorus matters in cannabis cultivation

Phosphorus is one of the three primary macronutrients (alongside nitrogen and potassium) that cannabis relies on to grow strong and healthy. While it's needed in smaller amounts than nitrogen, phosphorus still plays a vital role throughout the plant's life cycle, from early root formation to explosive bud development during the later flowering stages.
In the vegetative stage, phosphorus supports vigorous root growth and helps the plant to establish a solid foundation. Without enough phosphorus, cannabis roots can become weak or underdeveloped, which can impact the plant's ability to absorb water and nutrients.
During flowering, phosphorus becomes even more critical. It fuels the production of buds by facilitating energy transfer within the plant (through ATP), encouraging healthy bloom formation, resin production, and overall potency. Of course, a lack of phosphorus at this stage can result in sparse flowers and diminished yields, which is something no grower wants to see.
For a broader look at how nutrients can influence cannabis cultivation, check out our cannabis nutrients essential guide.
Signs of phosphorus deficiency in cannabis
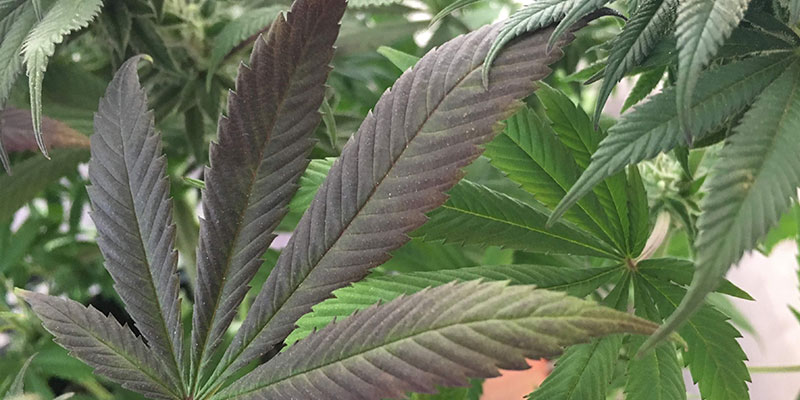

Phosphorus deficiency in cannabis can sneak up on growers of all experience levels. Because symptoms often begin subtly, it's essential to understand what to look for before the problem escalates.
A healthy cannabis plant typically boasts vibrant green leaves and consistent, vigorous growth. In contrast, a phosphorus-deficient plant starts to exhibit a very different profile.
One of the earliest and most noticeable signs is the purpling or reddening of stems and petioles, often in young plants. This change may be mistaken for genetics or environmental stress, but it's a key red flag. As the deficiency progresses, leaves will take on a dark, bluish-green hue that appears dull and lifeless rather than lush and healthy. Growth may noticeably slow or become stunted, especially in regions like the lower branches and roots, where phosphorus is most critical for development.
In more advanced stages, the edges of the leaves begin to bronze or brown, indicating cellular damage. This is typically followed by premature leaf drop, starting from the lower parts of the plant and working upward. During flowering, the impact becomes even more pronounced. Buds may remain weak, airy, and underdeveloped, severely affecting yield, flavour, and potency.
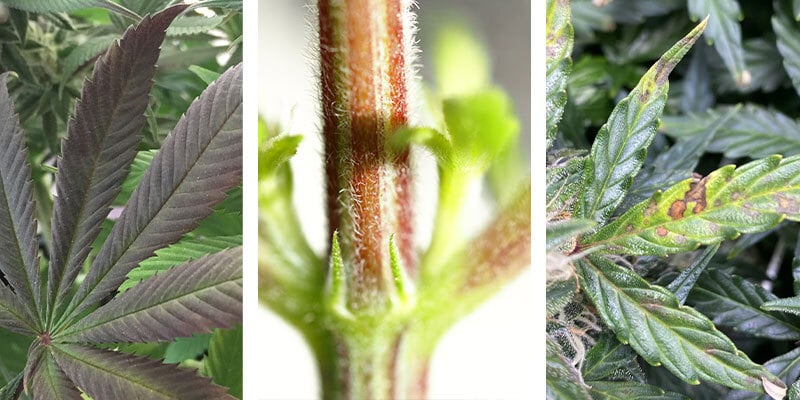

Quick reference: Phosphorus deficiency symptom checklist
- Purple/red stems and leaf stalks
- Slow vertical growth
- Dull, dark-green foliage
- Lower leaf discolouration or spotting
- Weak root development
- Reduced bud size and density
If you notice any of these signs, it's time to act fast. For a more comprehensive look at a variety of nutrient issues, visit our nutrient deficiencies guide.
Causes of phosphorus deficiency
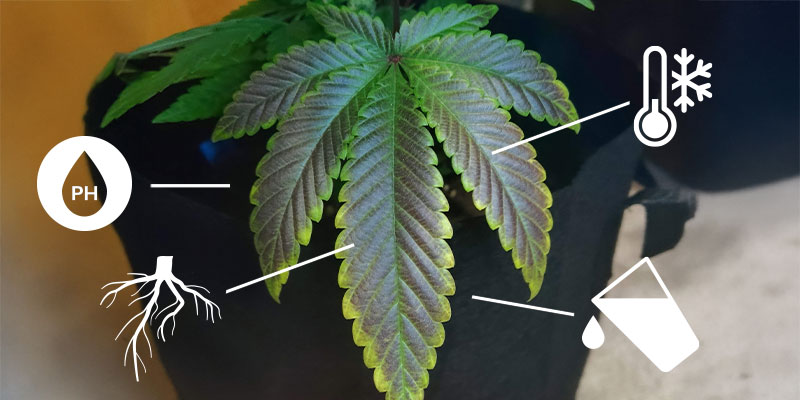

Phosphorus deficiency in cannabis isn't always the result of underfeeding. In many cases, growers are providing enough nutrients, but something in the environment or setup is stopping the plant from accessing what it needs. Understanding the root causes is key to correcting and avoiding the problem in the future.
pH imbalance
One of the most common reasons phosphorus becomes unavailable to cannabis plants is due to an incorrect pH level in the root zone. Cannabis thrives in slightly acidic conditions, with an optimal soil pH between 6.0 and 7.0 (or 5.5–6.5 in hydro setups). If the pH drifts outside this range, especially too low, phosphorus can become “locked out”, meaning it's present in the soil but chemically inaccessible to the plant.
Cold temperatures
Phosphorus uptake slows dramatically in cold conditions. When root temperatures drop below 15°C (59°F), plants struggle to absorb this nutrient even if it is abundantly available. Outdoor growers or those in poorly insulated grow rooms often encounter this issue during early spring or the late flowering stage. This is why phosphorus deficiency tends to occur more often in cooler climates or off-season grows.
Overwatering or compacted soil
When soil is constantly saturated or densely packed, oxygen levels around the roots drop, resulting in a suffocating environment that can hamper nutrient uptake. Overwatering and poor drainage can both lead to root stress and restrict the plant's ability to draw in phosphorus effectively. Similarly, compacted soils can prevent roots from expanding and functioning properly.
Poor nutrient absorption
Even when the grow medium is properly balanced and watered, plants might still fail to absorb phosphorus effectively if they're under stress. This could be due to root damage, pest infestations, or imbalanced feeding schedules. A deficiency of key micronutrients such as calcium and magnesium can also interfere with phosphorus metabolism, compounding the issue.
How to fix phosphorus deficiency in cannabis
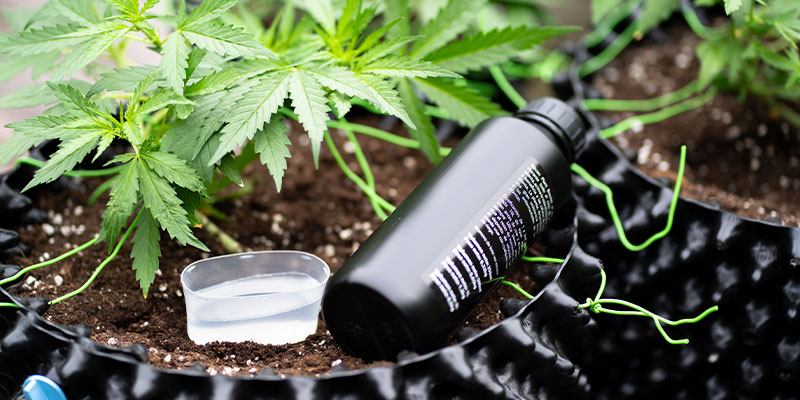

Correcting a phosphorus deficiency in cannabis involves more than simply adding more nutrients. To bring your plant back to full health, you must first diagnose the underlying issue, make targeted adjustments, and monitor recovery closely. Here's how to do it effectively.
- Confirm the symptoms
Start by verifying that the signs you're seeing match a phosphorus deficiency and not another nutrient issue. Cross-check with symptom charts and inspect your growing conditions. - Test and adjust the pH level
Next, test the pH level of your soil or hydroponic solution. If the pH is outside of the ideal ranges mentioned above (6–7 for soil; 5.5–6.5 for hydro), phosphorus can become chemically inaccessible, even if it's present. Use pH up or down products to gradually bring levels back into the optimal range, as sudden changes can shock your plants and cause further damage. - Evaluate temperature and environment
If you're growing in a cooler environment, check root zone temperatures. If they're consistently below 15°C (59°F), consider using heat mats, insulation, or moving your plants to a warmer spot. Warmer roots absorb nutrients more efficiently than cooler ones. - Improve drainage and soil structure
If your soil feels soggy or compacted, your plants may be oxygen-starved. Let the medium dry out slightly between watering, and consider amending it with perlite or coco coir to improve aeration and drainage. Avoid heavy watering routines that leave roots submerged for extended periods. - Apply a phosphorus-rich fertiliser
Once environmental and pH conditions are optimised, apply a high-quality fertiliser rich in phosphorus. Products with a higher middle NPK number (like 4-8-4 or 10-30-10) are ideal. Use according to the manufacturer's guidelines to avoid overfeeding. Zamnesia offers a wide selection of phosphorus-rich fertiliser options specifically formulated for cannabis growers. - Monitor and adjust
After treatment, monitor your plants over the following days and weeks. New growth should appear healthier, with better leaf colour and more vigorous development. Remember that damaged leaves won't recover; focus on how new leaves and shoots respond.
Restoring the phosphorus balance takes time, but with the right intervention, your plants can bounce back strong and healthy.
Preventing future deficiencies
Detecting and correcting a phosphorus deficiency is one thing, but prevention is your best friend here. Consistent care and a well-managed growing environment can go a long way in keeping your cannabis plants healthy and nutrient-balanced from seedling to harvest.
Regularly test your soil
Regular soil testing and monitoring are one of the most effective ways to prevent future nutrient issues. Use a reliable pH and EC meter to check the condition of your grow medium and nutrient solution. By staying on top of pH levels and salinity, you can avoid the common pitfalls that lead to nutrient lockout, including phosphorus unavailability.
Use quality nutrients and growing media
Choosing high-quality nutrients and growing media is equally important. Opt for cannabis-specific fertilisers with balanced NPK rations appropriate for every stage of growth. During flowering, switch to a bloom formula that provides extra phosphorus to support healthy bud formation. Avoid overusing your fertilisers, as salt buildup can impact nutrient uptake and mimic deficiency symptoms.
The base you grow in also matters. Poor-quality or heavily reused soil may lack the necessary structure and nutrient content to support vigorous cannabis growth. Invest in premium substrates designed for cannabis, which offer the right balance of drainage, aeration, and nutrient retention. You can explore different cannabis growing substrates with Zamnesia to find the perfect fit for your setup and experience level.
Ultimately, keeping your plants happy and phosphorus levels stable is all about consistency, providing a balanced diet, maintaining environmental conditions, and responding to changes before they escalate into full-blown deficiencies.
Phosphorus: An essential macronutrient

Phosphorus might not always be top of the list of many cannabis discussions, but it does play an essential role in every stage of cannabis cultivation. From establishing a strong root system to supporting dense, resin-rich buds, this macronutrient is critical for a plant's health, structure, and yield.
As we've seen, phosphorus deficiency in cannabis can manifest through subtle yet significant signs, such as discoloured stems, sluggish growth, and poor flowering performance. Fortunately, with the right knowledge and a proactive approach, it's a problem that any grower can overcome.
Staying vigilant is vital. By regularly checking your pH, monitoring environmental conditions, and using high-quality nutrients, you can prevent deficiencies before they start. Don't sit by and wait for symptoms to appear; build a strong nutritional foundation from the beginning of your grow, as soon as those tiny seedlings begin to sprout!
If you want to fortify your plants or fine-tune your feeding routine, explore our range of phosphorus-rich fertilisers and diagnostic tools. Whether you're growing in soil, coco, or hydro, Zamnesia has the resources and products to support every stage of your cannabis journey.
Empower your grow with the right tools, and your plants will reward you with strength, vitality, and some outstanding harvests that are well worth the extra level of care and vigilance.





 United States
United States











