
What Is The Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system is a fascinating network of channels and receptors that spans the length and breadth of the human body. Involved in everything from cognition and learning to appetite and immune response, it is essential and poorly understood. Find out all about it, and its relationship to cannabis.
Ever wondered how weed interacts with the body? The answer is complex and fascinating. In fact, the system it interfaces with has come to be named after it: the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
The ECS is a network of channels, receptors, and enzymes found throughout the body; from the brain and nervous system to the immune system, reproductive system, and beyond. It has numerous purposes, many of which we barely understand. Endocannabinoid signalling is chief among them, essentially making the ECS a body-wide channel of communication. But it goes far deeper than that.
In what follows, we break down all you need to know about the human endocannabinoid system.
What exactly is the endocannabinoid system?

In 1988, Allyn Howlett and William Devane found the first cannabinoid receptor in a rat's brain. Shortly thereafter, they were found in humans. Isolated THC was then used to further map the location of cannabinoid receptors within brains. Then, by deactivating certain receptors in rat brains, the CB1 receptor was identified as the one to which THC binds, causing its effects.
It was discovered in 1992 that there is an entire network of endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors, which together form the endocannabinoid system. Part of this discovery was the realisation that cannabinoids are produced naturally in the body—hence the receptors. The body’s own cannabinoids are called endogenous cannabinoids, aka endocannabinoids—“endo” meaning “within”. The first of these endocannabinoids to be discovered was anandamide, aka the "bliss molecule". "Ananda" is a word taken from Sanskrit that translates as "bliss".
In 1993, the second cannabinoid receptor, CB2, was discovered. In 1995, the second endocannabinoid, 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), was identified by Raphael Mechoulam and his team. The ECS has also been found in other animals, insects, and plants.
This complex system was indeed named after cannabis, which played an integral role in its discovery.
Why homeostasis is important

The role of the ECS is vast and nowhere near fully elucidated. That said, many scientists have come to agree that one of its main functions is the maintenance of homeostasis (Zou & Kumar, 2018). Homeostasis describes a state of balance, or “dynamic equilibrium”, within the body. Homeostasis is important as it maintains the proper and regular function of the body’s processes.
In the brain, endocannabinoids are retrograde signallers. This means that they fire from the receiving neuron back to the sender. They do this in order to modulate the amount of the incoming neurotransmitter. Essentially, if there is too much of it, they tell it to calm down, thus restoring equilibrium. This is one very simple example of how the ECS affects homeostasis.
Endocannabinoid system vs endocrine system
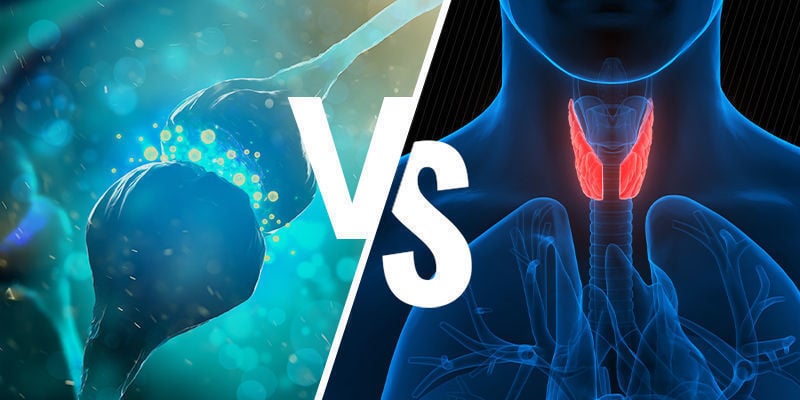
The endocrine system stems mostly from the thyroid gland and the adrenal gland. It too is a messenger system, but it works a little differently. The target of the endocrine system is predominantly organs, and it uses hormones (like the ECS uses endocannabinoids) for signalling. And while the ECS produces endocannabinoids in cell membranes, which then communicate with nearby cells, the endocrine system releases hormones into the bloodstream, which are then taken to different organs.
A good example of this is sympathetic arousal, also known as the fight or flight response. This well-known fear response, characterised by an increase in heart rate and breathing, sweaty palms, and sometimes shaking, is caused when the adrenal gland releases adrenaline into the bloodstream, where it signals to the necessary organs that it’s time to start going into overdrive, thus creating these physical responses.
What does the endocannabinoid system regulate?

The purported breadth of the ECS’ influence is really quite astonishing. Given how little we’ve known about it until recently, it’s surprising that it seems to interact with so many mental and physical functions.
The following list is by no means conclusive, but some functions the ECS is thought to influence include sleep (Corroon & Felice, 2019), immune response (Toguri, Caldwell & Kelly, 2016), pain (Toczek & Malinowska, 2018), and stress (Ruehle et al. 2012).
How does the endocannabinoid system function?
The ECS is more than just receptors and endocannabinoids—though these are the key pieces that make it function. Furthermore, endocannabinoids are not the only molecules that can interact with this internal system. Here we look at each part of the ECS in greater detail.
Endocannabinoids
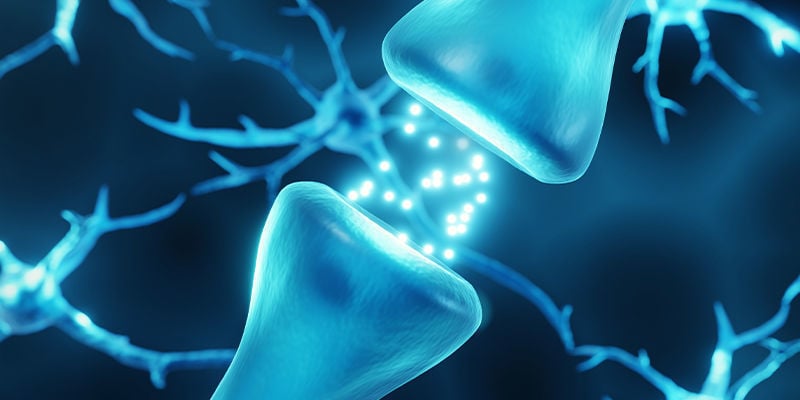
As mentioned, endocannabinoids work as signalling molecules within the ECS. To date, there are only two that are well-understood. These are N-arachidonoylethanolamide (anandamide) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
Anandamide plays a very broad role. It is a full agonist of CB1 receptors in the central nervous system (CNS) and a partial agonist of CB2 receptors in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The scope of its functions is not yet understood, but anandamide gains its name from the feelings of bliss and calm it causes when it is released, perhaps due to its potential role in the reward system. It also has some affinity to the body’s vanilloid receptors. More recently, it has been discovered that anandamide also binds to TRPV1, but more on this shortly.
2-AG is a full agonist of both the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Like anandamide, its exact functions are not fully understood. Indeed, it is not even known whether anandamide or 2-AG are primarily responsible for signalling within the ECS. What is known is that 2-AG is found in higher concentrations within the brain.
The other endocannabinoids (or suspected endocannabinoids) are:
- 2-Arachidonyl glyceryl ether (noladin ether)
- N-Arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA)
- Virodhamine (OAE)
- Lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI)
Metabolic enzymes

As endocannabinoids are produced as necessary to regulate different functions, they must also be broken down as necessary, once they’ve successfully played their role. This is where metabolic enzymes come in.
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is the enzyme responsible for breaking down anandamide. Indeed, although CBD affects the ECS in many ways, one of the main mechanisms is thought to be inhibiting FAAH, thus reducing the speed at which anandamide is broken down.
Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) breaks down 2-AG. Between FAAH and MAGL, the ECS itself is regulated, allowing it to effectively regulate many of the body’s functions and processes.
Cannabinoid receptors

There are currently two accepted cannabinoid receptors: CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are found most abundantly in the brain and central nervous system, whereas CB2 receptors are found most abundantly in the peripheral nervous system and immune cells. Between the two of them, they cover most of the body.
TRP channels
Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels also have a role to play in the ECS. These ion channels are found in the plasma membrane on many animal cells, and the TRPV1 (vanilloid) receptor is of particular interest when it comes to the ECS.
Both anandamide and CBD interface with TRPV1, which has led to some controversy over its classification. Generally, TRP channels are considered to be part of the expanded endocannabinoid system—but some now think that TRPV1 is an essential part of it (Iannotti & Vitale, 2021).
Phytocannabinoids

Strictly, phytocannabinoids are not part of the ECS. But they can have such a profound (and well-known) effect on it that we’ll include them here. “Phyto” simply means “plant”—so phytocannabinoids are cannabinoids from plants. Cannabis is not the only species of plant known to produce cannabinoids, but it produces them in the greatest abundance, and with the greatest variety.
To date, around 120+ distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated. Of these, we understand few to any great extent. The role that cannabinoids play in the life of a cannabis plant is uncertain, though it is speculated that they help to defend it from predators, provide resistance to sunlight, and more.
Interestingly, cannabinoids are produced in glands—called trichomes—on the surface of the cannabis plant, mostly on the flowers. In fact, the concentrations of cannabinoids found in the trichomes would be toxic to the rest of the plant, hence their position.
In the human body, these cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system to produce all manner of subtle to highly discernible effects.
How to impact the endocannabinoid system
So, it’s clear that we can manipulate the endocannabinoid system with phytocannabinoids. Whether this is a good idea or not differs from person to person, and we do not know enough about the interactions yet to say exactly what effect one cannabinoid will have, nor whether it could be beneficial. That said, we will do our best to explain possible mechanisms.
THC

Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the cannabinoid responsible for getting us high. It is one of the few cannabinoids capable of causing an intoxicating effect, so it seems fortunate that it is also the most abundant in cannabis plants.
THC works by mimicking anandamide and binding to the CB1 receptors. However, unlike anandamide, it is not easily broken down by FAAH. As a consequence, it is much more potent and longer-lasting than anandamide.
Of all the known ways to manipulate the ECS, THC is both the most extreme and the most common method.
CBD / CBDA
Cannabidiol (CBD) and its precursor cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) are catching up with THC for the position of the most popular cannabinoid.
In recent years, the CBD industry has exploded. Though in its infancy, research surrounding CBD has pinpointed several potential interactions with our ECS. However, CBD appears not to activate cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) in the traditional sense, instead working as an antagonist or inverse agonist. Effectively, it works to block the same receptor that THC wishes to bind to (CB1).
Given this mechanism, CBD (the second most abundant cannabinoid in cannabis) can be thought of as “counteracting” the effects of THC, at least to some degree (Niesink & van Laar, 2013). While this exact relationship is little understood, it is speculated that increasing the concentrations of CBD in recreational cannabis strains could make them better suited to more individuals.
Apart from classical endocannabinoid receptors, CBD, as mentioned earlier, is also believed to show some interaction with TRPV1 receptors, which are compelling in their own right.
CBN

Cannabinol (CBN) is usually only present in trace amounts in cannabis plants. It becomes more abundant as THC breaks down. This can happen naturally as cannabis flowers are left to age on the plant, via decarboxylation (heating), or through poor drying and curing practices.
CBN is thought to interact with the endocannabinoid system in a similar fashion to THC, but with lower affinities to both receptors. And unlike THC, CBN is not believed to be intoxicating, at least on its own.
THCV
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is also found in trace amounts, and is little understood. However, it is thought to be one of the few other cannabinoids that may be psychoactive. This is contested, though, and further research is necessary to conclude whether it is (Abioye et al., 2020).
THCV is an inverse agonist/selective antagonist of the CB1 receptor. The reason it is difficult to say whether it’s psychoactive or not is due to the generally low concentrations of THCV in cannabis. To test it, a huge amount has to be isolated and extracted, then given to participants. There are some anecdotal accounts to suggest that THCV is in fact psychoactive, and that the effects are shorter-lasting and more clear-headed than a THC high.
CBG / CBGA
Cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is the cannabinoid from which all others stem. It interacts with various enzymes and branches off into different “families”, ultimately becoming one or another type of cannabinoid (CBD, THC, CBG, etc).
Research into the effects of CBG is scant. What we do know is that it appears to interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors and antagonise the 5-HT1A serotonin receptor.
CBC
Cannabichromene (CBC) is a poorly understood cannabinoid. We do know that it is non-intoxicating, and we also know that it does not affect CB1 or CB2 receptors in the traditional sense. Instead, it appears to interact with TRPV1 and TRPA1, affecting their ability to break down endocannabinoids such as anandamide and 2-AG.
Should you be worried about clinical endocannabinoid deficiency?

As knowledge of the ECS increases, there has been a growing conversation surrounding “clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CECD)”. This theory—which posits the potentially pathological nature of having low endocannabinoid “tone”—has been linked to chronic illnesses such as irritable bowel syndrome, migraine, and fibromyalgia (Russo, 2016). Given the reach that the ECS has, pathological disruption or malfunction of this system could have negative effects on our health.
But before you reach for your weed to get some more cannabinoids into your system, understand that even if this condition does exist, it is little understood. Of course, if you find that weed has a positive effect on your life, that's great—but it’s best not to diagnose yourself with something so poorly elucidated. That said, study on CECD is growing, and researchers are hoping to uncover more details about the ECS and these difficult-to-treat conditions.
- Abioye, Amos, Ayodele, Oladapo, Marinkovic, Aleksandra, Patidar, Risha, Akinwekomi, Adeola, Sanyaolu, & Adekunle. (2020, December). Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV): a commentary on potential therapeutic benefit for the management of obesity and diabetes - https://jcannabisresearch.biomedcentral.com
- Corroon J, & Felice JF. (2019 Jun). The Endocannabinoid System and its Modulation by Cannabidiol (CBD) - https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Iannotti, Fabio Arturo, Vitale, & Rosa Maria. (2021/3). The Endocannabinoid System and PPARs: Focus on Their Signalling Crosstalk, Action and Transcriptional Regulation - https://www.mdpi.com
- Niesink, Raymond J.M., van Laar, & Margriet W. (2013/10/16). Does Cannabidiol Protect Against Adverse Psychological Effects of THC? - https://www.frontiersin.org
- Russo, & E. B. (2016). Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency Reconsidered: Current Research Supports the Theory in Migraine, Fibromyalgia, Irritable Bowel, and Other Treatment-Resistant Syndromes. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, 1(1), 154–165. - https://www.liebertpub.com
- S Ruehle, A Aparisi Rey, F Remmers, & B Lutz. (2012, January). The endocannabinoid system in anxiety, fear memory and habituation. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 26(1), pp.23-39. - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Toczek, M. and Malinowska, & B. (2018/07/01). Enhanced endocannabinoid tone as a potential target of pharmacotherapy - https://www.sciencedirect.com
- Toguri, James T., Caldwell, Meggie, Kelly, & Melanie E. M. (2016/09/15). Turning Down the Thermostat: Modulating the Endocannabinoid System in Ocular Inflammation and Pain - https://www.frontiersin.org
- Zou, Shenglong, Kumar, & Ujendra. (2018/3). Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System - https://www.mdpi.com
-
 6 min
9 April 2024
What Is The Entourage Effect?
A product of the 1990s, the theory of the entourage effect is arguably one of the hottest topics of discussion in the cannabis world. Click here for an overview of the entourage effect and what...
6 min
9 April 2024
What Is The Entourage Effect?
A product of the 1990s, the theory of the entourage effect is arguably one of the hottest topics of discussion in the cannabis world. Click here for an overview of the entourage effect and what...
-
 3 min
3 December 2021
What Is Delta-8 THC (∆⁸-THC)?
With so many cannabinoids in cannabis, it's only a matter of time before they're all thoroughly researched and utilised. With unique effects and potential benefits, one such cannabinoid that's...
3 min
3 December 2021
What Is Delta-8 THC (∆⁸-THC)?
With so many cannabinoids in cannabis, it's only a matter of time before they're all thoroughly researched and utilised. With unique effects and potential benefits, one such cannabinoid that's...






 United States
United States











